GPU Explained: Revolutionizing Computing & Gaming
Table of Contents
Have you ever marveled at the seamless rendering of graphics-heavy games or the smooth operation of expansive virtual universes like Minecraft on a standard computer? The secret behind these wonders lies in a single acronym: GPU.
Deciphering GPU: Unveiling its Significance
In this piece, we unravel the enigma of GPU – the Graphics Processing Unit – by exploring its functionalities and diverse applications. Without further delay, let’s plunge into this fascinating world!
What Constitutes a GPU?
A GPU, or Graphics Processing Unit, stands as a computational powerhouse adept at handling massive parallel processing loads, primarily catering to graphics-centric tasks. Functioning as a self-contained computational environment, the GPU boasts its processing cores and memory, making it a pivotal element in scientific computations and mathematical operations.
The crux of graphics processing relies heavily on mathematics, where colors are mere numerical representations within matrices. This mathematical essence enables GPUs to seamlessly execute graphics-related tasks.
The Role of GPUs Across Diverse Fields
Predominantly recognized in the gaming realm for their utilization in delivering captivating visual experiences, GPUs extend their prowess to critical sectors like medical imaging. Here, precision and rapid data processing stand as paramount requisites, wherein GPUs excel.
Diverse GPU Categories
Before delving into their attributes, let’s distinguish between the two prevalent GPU types:
Integrated GPU: A Compact Solution
Integrated GPUs reside within the computer’s motherboard, offering compactness, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Ideal for basic graphic operations, they, however, marginally lag behind dedicated GPUs due to the latter’s specialized ecosystem and enhanced performance mechanisms.
Discrete GPU: Unveiling Enhanced Performance
Operating as standalone chipsets connected to the system via a connector, discrete GPUs boast dedicated cooling systems, ensuring superior performance. Despite their higher price point, they stand as the preferred choice for intensive tasks like video processing and high-end gaming.
Decoding GPU versus CPU
Understanding the distinction between GPU and CPU is pivotal:
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
Tasked primarily with processing graphics-oriented data, GPUs possess an architecture housing numerous low-capacity processing cores. This abundance of cores expedites parallel computations, ensuring high throughput and swift execution of complex tasks.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Contrarily, CPUs are versatile, general-purpose chipsets governing all system operations. With a limited number of high-performance cores, they excel in serial processing tasks, ensuring rapid execution of non-parallel operations.
Salient Features of GPUs
Let’s explore the key advantages offered by GPUs:
Empowering Graphics-Intensive Tasks
GPU’s forte lies in handling graphics-centric tasks with superior parallel processing capabilities, relieving the main CPU and enhancing performance for tasks like photo/video editing and running high-end games.
Expeditious Complex Calculations
Capable of executing intricate graphics-based calculations swiftly, GPUs find relevance in scientific computations, data analytics, and even machine learning. Their processing acceleration surpasses traditional CPUs, particularly in heavy machine-learning tasks.
Multifunctional Nature
Beyond graphics, GPUs extend their utility to various tasks. When applications support GPU processing, offloading CPU-intensive tasks onto the GPU effectively augments system capabilities, acting as supplementary CPU and memory resources.
Limitations of GPUs
Despite their prowess, GPUs encounter certain constraints:
Cost Factor
The superior performance and additional assets embedded in GPUs elevate their cost compared to CPUs, presenting a significant financial disparity.
Need for Independent Cooling
GPU’s independent cooling mechanisms—be it heat sinks, fans, or liquid cooling—additionally inflate maintenance costs, unlike standard CPUs reliant on simpler cooling mechanisms.
Compatibility Challenges
Not all applications seamlessly utilize GPU for processing-intensive tasks, limiting their efficacy. However, ongoing developments hint at broader software support for GPU-based processing in the future.
Diverse Applications of GPUs
The versatility of GPUs extends to various domains:
- Gaming: Unrivalled in powering high-end games, GPUs offer the processing capacity indispensable for immersive gaming experiences.
- Media Editing: Leveraging their innate graphic prowess, GPUs expedite the editing and processing of photos and videos, surpassing CPU performance.
- Machine Learning Model Training: In the realm of machine learning, GPUs prove instrumental in swiftly executing iterative mathematical calculations, and expediting model training processes.
In essence, GPUs, with their robust capabilities, revolutionize various industries, from gaming to scientific research, promising accelerated and dynamic processing power.
Let’s delve deeper into the realm of GPUs, understanding their mechanics and far-reaching impact across diverse applications.
How to Easily Identify Your GPU
Are you unsure about the GPU specifications powering your system? Knowing your Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) details is vital, especially if you’re into gaming or high-performance tasks. Let’s explore simple methods to identify your GPU, whether you’re using Windows or Mac.
Windows: Unveiling Your GPU Details
For Windows users, discovering your GPU specifics is a straightforward process. Utilize the DirectX Diagnostic Tool to unveil the crucial information.
- Press Windows+R to summon the Run window.
- Type dxdiag and hit Enter.
- Once the DirectX Diagnostic Tool opens, click on the Display tab.
- Here, you’ll find detailed data such as the GPU’s name and manufacturer.
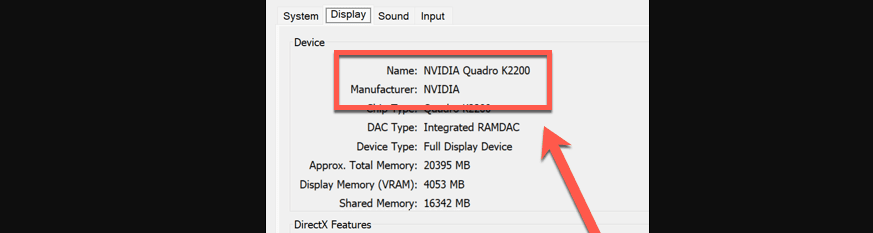
To delve deeper into your device’s specifications, consider conducting a web search using your specific model as a query.
Mac: Unveiling GPU Details on Your Mac System
Mac users, uncovering your GPU details is equally accessible through the Apple menu.
- Open the Apple menu.
- Select About This Mac.
- Under the Overview tab, spot the GPU currently in use, mentioned next to Graphics.
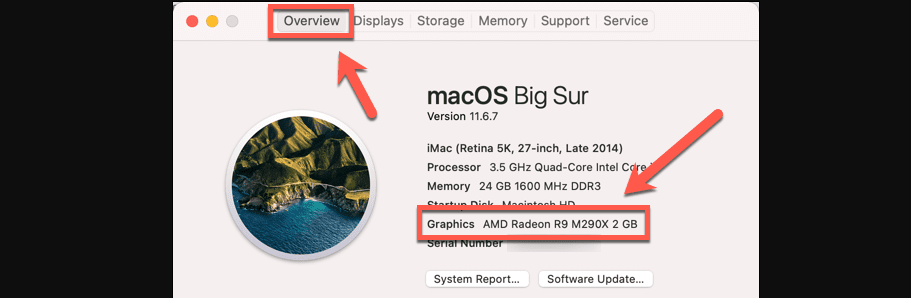
- Click on System Report to acquire more insights.
- Navigate to Hardware and click on Graphics/Displays for an expanded view of your GPU information.
Understanding your GPU’s capabilities and specifications not only helps in assessing game compatibility but also aids in monitoring performance during resource-intensive activities like 3D gaming. Whether it’s Windows or Mac, easily accessing this information ensures you make informed decisions about your system’s capabilities.
Remember, staying updated about your GPU’s specifics allows you to optimize your computing experience. So, go ahead and explore your GPU details today!
What exactly is a GPU, and how does it differ from a CPU?
A GPU, or Graphics Processing Unit, is a specialized computing device designed for handling large volumes of parallel processing, especially for graphics-related tasks. Its architecture, with numerous low-capacity cores, contrasts sharply with a CPU (Central Processing Unit), which has fewer high-performing cores. While GPUs excel in parallel computations, CPUs are more adept at serial processing tasks.
What are the primary applications of GPUs beyond gaming?
GPUs have expanded their influence beyond gaming into various fields. They are extensively utilized in medical imaging for their precision and rapid processing capabilities. Moreover, they excel in tasks like video editing, data analytics, machine learning model training, and scientific computations due to their ability to execute complex calculations swiftly.
How do integrated GPUs differ from discrete GPUs, and what advantages do they offer?
Integrated GPUs are compact chipsets integrated into a computer’s motherboard, offering energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. However, they slightly underperform compared to discrete GPUs due to the latter’s dedicated ecosystem and enhanced performance mechanisms. Integrated GPUs suit basic graphic tasks, while discrete GPUs, operating as standalone chipsets with dedicated cooling systems, excel in intensive tasks like video processing and high-end gaming.
What are the limitations associated with using GPUs?
Despite their remarkable capabilities, GPUs come with certain limitations. They are generally costlier than CPUs due to their specialized architecture and added assets. Additionally, GPUs necessitate independent cooling mechanisms, which can inflate maintenance costs. Furthermore, not all applications seamlessly support GPU-based processing, limiting their utilization in certain scenarios.
What diverse applications can GPUs be used for apart from gaming?
GPUs find applications across various domains. They are instrumental in powering high-end gaming experiences, expediting media editing tasks such as photo and video editing, and training machine learning models. Their multifunctional nature enables them to accelerate diverse computational tasks, promising increased system capabilities when utilized effectively.
In conclusion
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) stand as transformative elements in the realm of computing, transcending their traditional role in gaming. Their significance lies in their ability to handle immense parallel processing loads, making them indispensable for graphics-related tasks and beyond. While integrated GPUs offer energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness for basic graphics tasks, discrete GPUs, with their dedicated architecture and superior performance, cater to high-demanding tasks like video processing and gaming.
However, despite their remarkable capabilities, GPUs come with certain limitations such as higher costs, the need for independent cooling mechanisms, and limited application support in some software ecosystems. Nevertheless, the versatile applications of GPUs extend beyond gaming, encompassing domains like medical imaging, machine learning, data analytics, and scientific computations. Overall, GPUs represent a crucial technological advancement, reshaping computing landscapes by providing accelerated and efficient parallel processing capabilities, and driving innovation across diverse industries.


