Solving High RAM Usage in Google Chrome on Windows
Table of Contents
If you’ve noticed your Google Chrome browser lagging and hogging up your computer’s RAM, worry not. Below are steps to effectively reduce the RAM usage by Google Chrome on your Windows computer.
Understanding the RAM Predicament
Google Chrome, by default, has a penchant for utilizing the maximum CPU and RAM available, ensuring optimal speed. While this is beneficial on high RAM capacity computers, it poses challenges on budget computers equipped with lower RAM.
Besides this default behavior, high RAM usage in Google Chrome can be attributed to multiple open tabs, incompatible browser extensions, a corrupted browser cache, and various other factors.
Step-by-Step Solutions
Close Excessive Browser Tabs
The more tabs you open, the more resources Chrome demands. Close unnecessary tabs, exit all running programs and reload the webpage to alleviate RAM strain.
Keep Chrome Updated
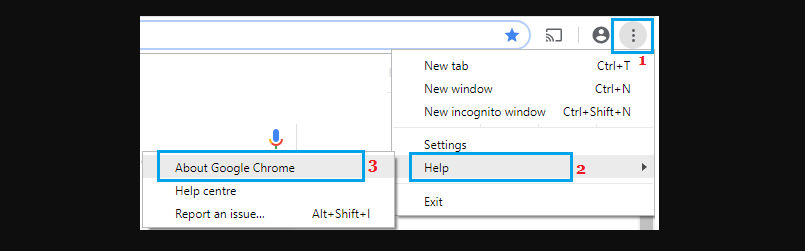
Ensure you’re using the latest Chrome version. Click on the three-dot menu icon, hover over Help, and select About Google Chrome. Allow Chrome to check for updates and apply them.
Clear Browser Cache
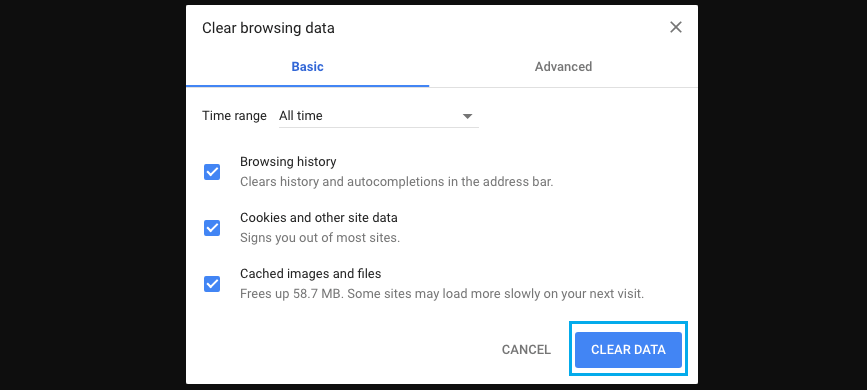
To eliminate expired or corrupted cached files causing high CPU usage, clear the browser cache. Click on the three-dot menu icon, go to More Tools, and select Clear Browsing Data. Choose “All Time” as the time range and clear history, cookies, site data, and cached images and files.
Disable Background Apps
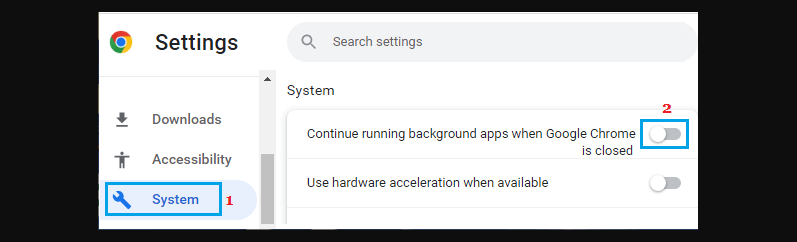
Prevent Chrome from allowing plugins and extensions to run in the background. Open Chrome settings, select System and disable the “Continue running background apps when Google Chrome is closed” option.
Check for Conflicting Software
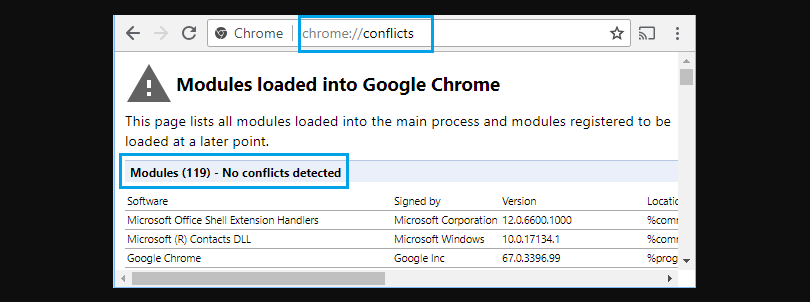
Type chrome://conflicts into the address bar to identify conflicting software. Uninstall the conflicting program via Settings > Apps > Program Name > Uninstall.
Turn Off Hardware Acceleration
On computers with low RAM capacity, hardware acceleration can be problematic. In Chrome settings, under System, disable the “use hardware acceleration when available” option.

Disable Browser Extensions
Incompatible browser extensions contribute to high CPU usage. In Chrome settings, go to More Tools > Extensions, disable or remove unnecessary extensions, and restart Chrome.
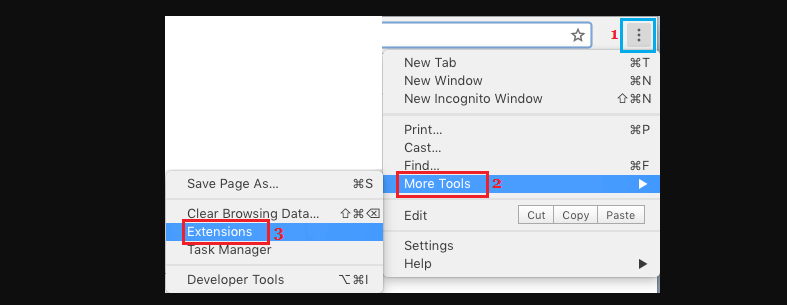
Reset Chrome to Default Settings
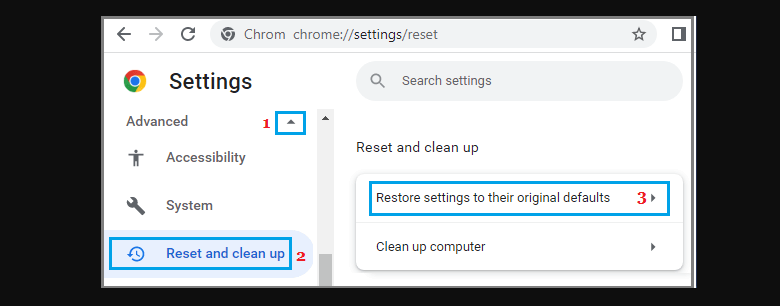
If the issues persist, reset Chrome to default settings. Open Chrome settings, navigate to the Advanced tab, select Reset & Clean Up, and click on “Restore settings to their original defaults.” Confirm the reset.
After resetting, reapply the steps to disable hardware acceleration and prevent Chrome from running in the background.
Conclusion
Tackling high RAM usage in Google Chrome involves a systematic approach. By following these steps, you can optimize Chrome’s performance on your Windows computer, ensuring a smoother browsing experience.
Why does Google Chrome use so much RAM?
Google Chrome prioritizes optimal performance by utilizing available system resources, often resulting in high RAM usage, especially on budget computers.
How frequently should I clear my browser cache?
Regularly clearing the browser cache is advisable for monthly maintenance, preventing the accumulation of expired or corrupted files.
Can I permanently disable hardware acceleration?
Yes, you can disable hardware acceleration in Chrome settings to address compatibility issues with low RAM computers.
Is resetting Chrome a common solution?
Resetting Chrome should be a last resort. If performance issues persist, it’s a viable option to restore default settings.
Are there alternative browsers with lower RAM usage?
Certainly, browsers like Mozilla Firefox or Opera are known for being less resource-intensive, providing alternatives for users with limited RAM.



